Shortwave Radio and Cryptography: The Secret Side of the Airwaves
Shortwave radio is a fascinating medium that has connected people across the globe for decades. It’s not just a platform for international broadcasters, amateur operators, and hobbyists—it also has a history steeped in mystery and secrecy. Welcome to the hidden world where shortwave radio and cryptography intersect, revealing a legacy of coded wartime messages, enigmatic numbers stations, and the enduring allure of decoding the unknown.
Cryptography Over the Airwaves: A Brief History
Since World War I, governments worldwide have used shortwave radio to send encrypted messages to their operatives across the globe. The medium’s ability to cover vast distances with a relatively simple setup made it an ideal choice for clandestine communications. Correctly decoding these messages required possession of a one-time pad or codebook—a key that unlocked the seemingly random streams of letters and numbers.
During World War II, this technique became even more refined. Allied and Axis forces alike used shortwave transmissions to communicate with spies, resistance fighters, and military units. The famous Enigma machine, used by Nazi Germany, is a prime example of cryptographic innovation intersecting with shortwave radio. While the Enigma codes were famously broken by Alan Turing and his team at Bletchley Park, many other ciphers remained undeciphered, adding to the mystique of wartime shortwave cryptography.
Numbers Stations: The Enigma of Modern Cryptography
One of the most intriguing aspects of shortwave radio is the mysterious phenomenon of numbers stations. These stations transmit sequences of numbers, letters, or tones in an almost hypnotic repetition, often read by an automated or synthesized voice. Sometimes, Morse code or digital formats are used instead. Their purpose? To deliver secret instructions to intelligence operatives.
Governments from countries such as Cuba, Russia, North Korea, Israel, the USA, and even former nations like Czechoslovakia have been known to use numbers stations. These transmissions are nearly impossible to trace back to their origin, making them a highly secure and anonymous method of communication. All a recipient needs is a shortwave radio, knowledge of the transmission’s time and frequency, and the corresponding codebook to decipher the message.
Numbers stations are shrouded in mystery and have captivated shortwave enthusiasts for decades. Some of the most famous stations include the “Lincolnshire Poacher,” thought to originate from the UK, and “UVB-76,” a Russian station also known as “The Buzzer.” Their cryptic broadcasts continue to fascinate listeners, sparking countless theories and debates.
To dive deeper into this enigmatic world, don’t miss our dedicated blog on numbers stations, where we explore their history, notable examples, and why they remain relevant in the modern age.
Why Shortwave and Cryptography Endure
In an era dominated by digital communication, why do shortwave radio and cryptography still matter? The answer lies in their simplicity and resilience. Shortwave transmissions are hard to intercept and jam, and they don’t rely on internet infrastructure or modern technology. This makes them an excellent backup for covert communications and an enduring symbol of secrecy.
For enthusiasts, the thrill of decoding a hidden message or stumbling upon a mysterious broadcast adds an element of adventure to shortwave listening. It’s not just about hearing voices from distant lands; it’s about uncovering secrets and connecting with a part of history that’s both fascinating and elusive.
Tune In and Decode the Unknown
Shortwave radio’s intersection with cryptography is a reminder that the airwaves hold more than just music and news—they carry secrets, stories, and a legacy of ingenuity. Whether you’re a history buff, a cryptography enthusiast, or a curious listener, exploring this hidden side of shortwave radio is a journey worth taking.
Grab your shortwave receiver, tune in, and who knows? You might just stumble upon the next great mystery waiting to be decoded.






 In the vast expanse of Death Valley National Park, a remote desert in southern California, modern connectivity often falls short. On a fateful Saturday, April 6, a family’s adventure took an unexpected turn when their vehicle became trapped in mud in a hazardous area, leaving them without cell service. In this critical moment, amateur radio proved to be their saving grace.
In the vast expanse of Death Valley National Park, a remote desert in southern California, modern connectivity often falls short. On a fateful Saturday, April 6, a family’s adventure took an unexpected turn when their vehicle became trapped in mud in a hazardous area, leaving them without cell service. In this critical moment, amateur radio proved to be their saving grace.


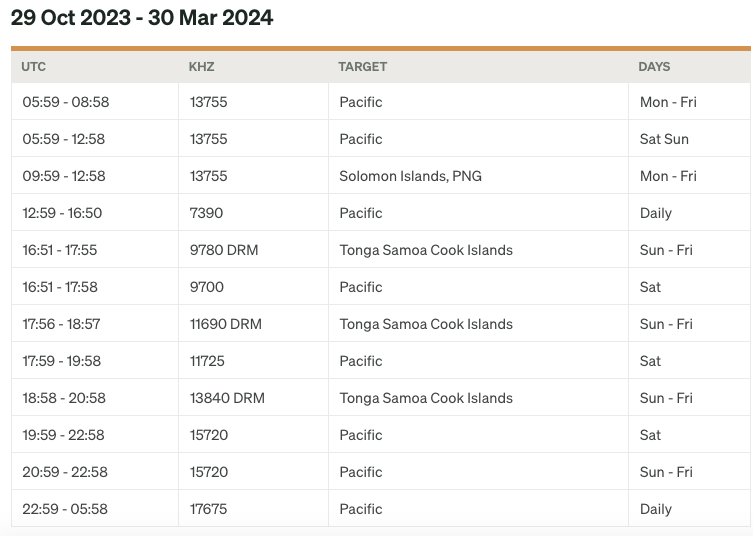
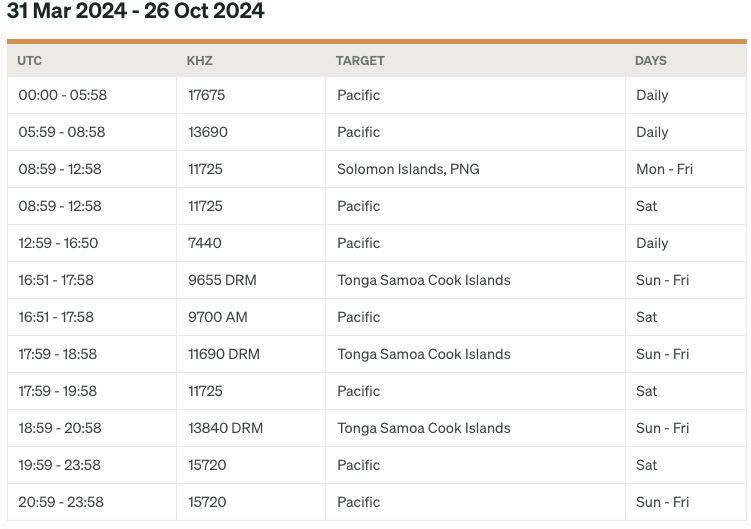
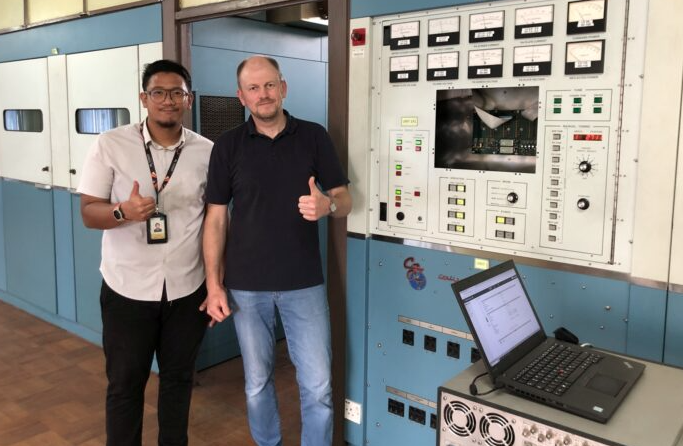
 If you’re captivated by unique radio facilities, then you’re in for a treat. Join us on a journey to discover one of the most picturesque shortwave transmitter sites nestled in the heart of the tropics. Today, we’re delving into the story of KTWR, a beacon of broadcasting excellence stationed on the tranquil shores of Guam. Inspired by a captivating article on RadioWorld.com, we invite you to immerse yourself in the enchanting world of shortwave broadcasting with us.
If you’re captivated by unique radio facilities, then you’re in for a treat. Join us on a journey to discover one of the most picturesque shortwave transmitter sites nestled in the heart of the tropics. Today, we’re delving into the story of KTWR, a beacon of broadcasting excellence stationed on the tranquil shores of Guam. Inspired by a captivating article on RadioWorld.com, we invite you to immerse yourself in the enchanting world of shortwave broadcasting with us.
