
Shortwave radio’s golden era spanned much of the 20th century, offering a unique portal to the world for listeners in New York, Moscow, Nairobi, Sydney, and beyond. Across cities and small towns, in apartments, rural villages, and sometimes even in secret, people would gather around radios, scanning for distant voices carrying news, culture, and perspectives. At a time when mainstream information channels were local or national at best, shortwave created a truly global media experience.
The Golden Era: News, Culture, and Education Across Borders
From the 1930s onward, international broadcasters leveraged shortwave to reach listeners worldwide, providing a flow of uncensored information and cultural exchange. In New York, listeners might tune into the BBC World Service for news from London, a fresh perspective on events shaping Europe and the world. Elsewhere, Radio Moscow (now Voice of Russia) broadcast to millions, offering the Soviet perspective to audiences from East Asia to the Americas. In Africa, Kenya Broadcasting Corporation began shortwave broadcasts in the 1950s, connecting people in remote areas to national news and global events. Meanwhile, in places like Eastern Europe, where media was tightly controlled, Radio Free Europe and Voice of America offered a rare opportunity to hear voices and viewpoints forbidden by local governments.
People would sit in living rooms or lean over rooftop antenna setups, adjusting dials to pick up broadcasts from Deutsche Welle in Germany, Radio Australia, or Radio Netherlands Worldwide. For many, tuning into Radio Havana Cuba or Radio Cairo was an educational and cultural experience—one that helped shape views of distant lands and ideologies. These broadcasts were often paired with music and language courses, enticing listeners with stories of far-off places while subtly sharing political or cultural messages.
Shortwave broadcasting reached every corner of the globe, connecting people from vastly different backgrounds. During times of political tension, such as the Cold War, it became a powerful tool for ideological influence. While the BBC aimed to promote British cultural diplomacy and impartial news, Radio Moscow and Voice of America promoted their respective ideologies, each vying for influence in regions like Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Decline in the Age of the Internet
With the advent of the internet, satellite TV, and other digital platforms, shortwave’s influence began to fade in the 1990s. Major international broadcasters shifted focus, directing funds toward newer forms of media. The BBC, for instance, significantly reduced its shortwave services, redirecting resources to digital platforms that could target specific demographics and offer interactive content. Stations like Radio Netherlands Worldwide and Radio Canada International eventually closed their shortwave services altogether.
Shortwave was also expensive. The infrastructure, transmitters, and energy required to reach far-off regions became less justifiable as internet and mobile networks expanded. By the early 2000s, many countries had scaled back or eliminated their shortwave operations, relying instead on the internet to reach global audiences. Yet, even in decline, shortwave retained a loyal following of enthusiasts and people in areas still beyond the reach of reliable internet access.
The Lasting Relevance of Shortwave Radio
Despite its diminished presence, shortwave continues to play an essential role where digital networks are inaccessible, censored, or unreliable. In countries with strict media restrictions, such as North Korea, Eritrea, and parts of the Middle East, shortwave remains a rare source of independent news. During natural disasters or political upheavals that compromise infrastructure, shortwave can provide life-saving information. The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami and the 2010 Haiti earthquake both highlighted shortwave’s unique utility, with international broadcasters like Voice of America quickly organising broadcasts to deliver crucial updates.
Shortwave’s enduring role is also evident in humanitarian and emergency contexts. Radio stations like BBC World Service and Radio Free Asia still maintain shortwave services specifically to reach audiences in countries where free press is restricted or where internet access is a luxury. For these regions, shortwave remains a lifeline to the outside world, delivering news, health information, and educational programming.
Shortwave’s Global Reach in the 21st Century
- Crisis Resilience: Shortwave is invaluable in emergency situations, often remaining operable when other infrastructure fails. During the recent conflict in Ukraine, for instance, international broadcasters revived shortwave services to provide reliable information to those affected by disruptions to local communications.
- Remote Accessibility:** Shortwave broadcasts reach places where other media cannot, making it a reliable means of access for people in rural or economically disadvantaged areas. In parts of South America, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asia, shortwave serves as a bridge to the broader world.
- Independence from Local Control:** Shortwave bypasses local government controls, allowing individuals in restricted environments to access information. In Iran, China, and Saudi Arabia, where government restrictions on media are common, listeners often rely on international shortwave broadcasts to gain alternative perspectives.
- A Diverse Global Community:** Shortwave radio fosters a distinctive global listening community. From enthusiasts across the United States to hobbyists in Japan, shortwave brings people together over vast distances and shared curiosity.
The Future of Shortwave Radio
Though shortwave may never regain its former dominance, it remains a crucial asset. The medium is also evolving, with digital shortwave technology promising clearer sound and more efficient broadcasting. Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) offers improved signal quality, and broadcasters are exploring ways to combine digital shortwave with new media. As technology advances, shortwave might even see a resurgence in areas where internet access remains unreliable or heavily monitored.
Shortwave radio’s enduring presence in international broadcasting reflects its ability to adapt, even as technology has reshaped media landscapes. For people in remote regions or repressive societies, shortwave is still a vital source of information and connection. While the future of international broadcasting may look very different, shortwave remains a powerful symbol of radio’s legacy in fostering global understanding, offering a voice across boundaries, and supporting people when and where it matters most.

Solar activity, such as sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), can significantly impact radio signals, particularly in shortwave and high-frequency (HF) bands. Here’s how it works:
- The Sun and the Ionosphere:
Radio waves rely on the Earth’s ionosphere (a layer of charged particles in the upper atmosphere) to bounce signals over long distances. Solar activity affects the ionosphere by increasing ionisation levels, which changes how well it can reflect radio signals.
- Improved Signal Propagation:
During periods of increased solar activity, when sunspots are numerous, the ionosphere becomes more reflective. This boosts the range of shortwave radio signals, due to reflection, allowing them to travel a greater distance.
- Signal Disruptions:
Solar flares and CMEs (Coronal Mass Ejections) can cause sudden ionospheric disturbances, which may lead to radio blackouts. These events can block or degrade radio signals, especially on the sunlit side of the Earth.
- Day vs. Night Propagation:
Solar radiation influences the ionosphere more during the day than at night. As a result, higher frequency signals (like shortwave) propagate better during daylight, while lower frequencies (like MW) tend to perform better at night.
- Solar Cycle Impact:
The Sun follows an 11-year solar cycle. During the peak (solar maximum), radio conditions improve, but disruptions also become more common. During solar minimum, signal ranges may be reduced. We are currently in Solar Cycle 25 with maximum activity expected in July 2025.
Understanding these solar influences helps radio enthusiasts optimise their listening experience by timing operations with favourable solar conditions.
The development of the modern phonetic alphabet for radio communication was developed and refined over the period from 1927 until 1965. Practical experience over both World Wars and subsequent conflicts involving voice radio communications have led to the final version used today, known officially as the NATO Phonetic Alphabet.
The phonetic alphabet consists of a collection of 26 code words, each representing a single letter of the alphabet. This system was devised and revised to ensure the use of the phonetic alphabet would eliminate any ambiguity during the passing of messages by radio (or telephone), and that the letters and numbers would be easily distinguishable from one another.
Over radio, the names of many letters sound similar, for instance “n” and “m”, “f” and “s” etc. Using the codeword for each letter improves readability in poor radio conditions.
The 26 code words of the phonetic alphabet are:
Alfa, Bravo, Charlie, Delta, Echo, Foxtrot, Golf, Hotel, India, Juliett, Kilo, Lima, Mike, November, Oscar, Papa, Quebec, Romeo, Sierra, Tango, Uniform, Victor, Whiskey, Xray, Yankee, Zulu
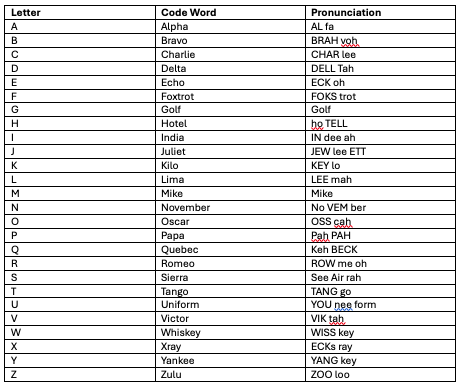
Emphasis is placed on the letters shown in capitals.
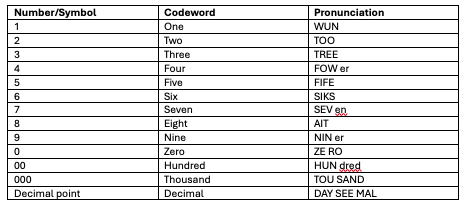
There are also codewords for numbers, to minimise miscommunication.
Number/Symbol Codeword Pronunciation
These code words are used today by amateur, aviation, marine and both civilian and armed forces.


